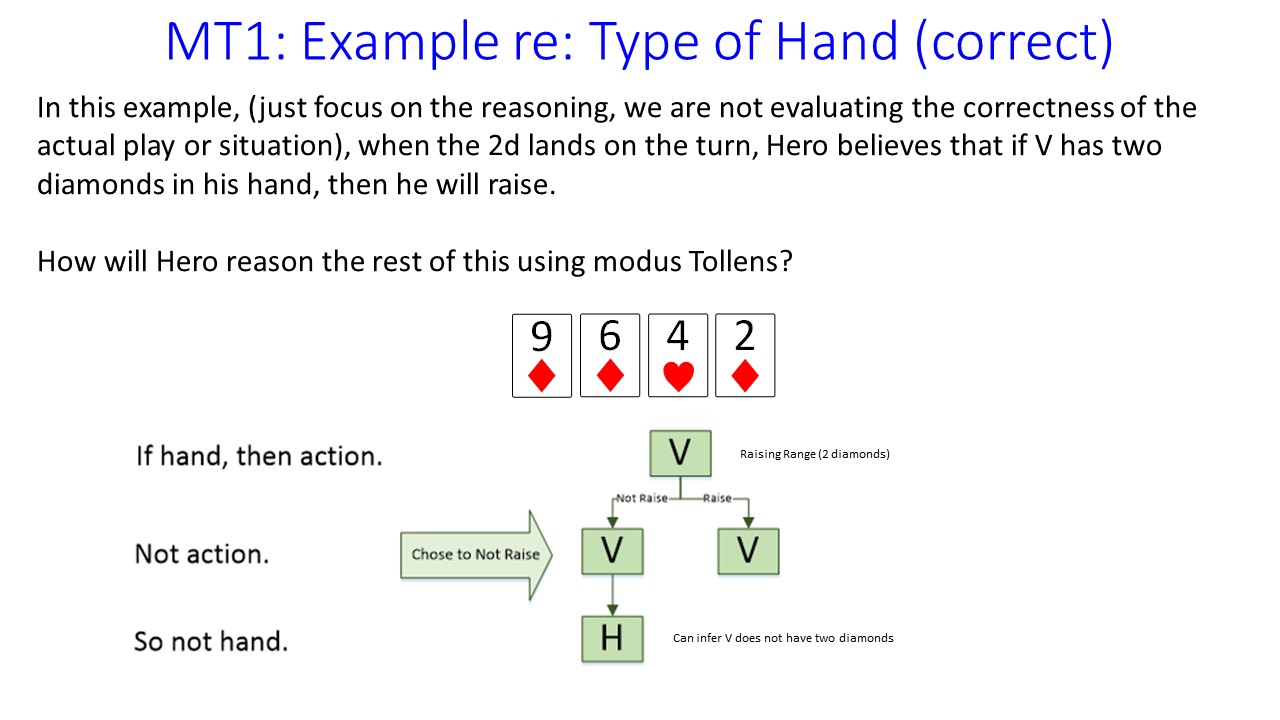
For those who aren’t very good at it, the ability to put a poker player on a hand is a tough concept to grasp, and when watching it done correctly, it appears mystical and almost magic-like. Misconceptions abound about the notion of determining what an opponent is holding, and many players even believe that the goal of putting a poker player on a hand is to deduce the precise two cards in his hand.
- Poker Hand Reading Practice
- Learn To Play Poker Beginner
- How To Read Hands In Poker
- How To Read Palms Hands Psychic
- Poker How To Read Hands Without
Nothing could be further from the truth. Although it’s uber-cool to be able to announce your opponent’s two hole cards to him, and very disconcerting for any opponent to be seen as that transparent, it neither happens very often nor is it very important in the overall scheme of playing winning poker.
Once you’ve learned the fundamental poker strategies, reading hands will be the skill that creates the most edge. If you can accurately read your opponents’ hands, your decisions of when to bet, raise call, bluff, etc. Will be more accurate, making them more profitable. The ability to read hand in online poker is actually at the height of mastering the poker game. Hand reading is at the expert level and only the pros are best at it. In the real sense, hand reading in online poker is a player’s ability to correctly guess another player’s hand or range of hands in any given situation. Hand reading, like any poker strategy, requires loads of practice before you turn it into a skill you can successfully use on the felt. Couple this with the fact that you’re making assumptions about a player’s range and how they play their hands, you’ll find yourself making lots of hand reading mistakes early on.
While you’ll occasionally run into a very uncreative opponent who plays as though his cards were face-up, and every now and then you’ll take a deductive stab at an opponent’s hand that hits the nail squarely on the head, just enjoy the moment because it doesn’t happen very often.
The key to putting a player on a hand is to know your opponent, and that means getting a fix on his playing tendencies. If you don’t know your opponent’s playing tendencies, you won’t be able to make an accurate assessment of his playing range in given situations. If you can’t decipher his style and playing tendencies, his hand will usually remain a mystery and you won’t have much of an idea how well your hand plays against his range.
If you’re playing poker correctly, you’ll be adjusting to your opponent’s style of play and as a result, it’s more important for you to arm yourself with knowledge, skill, and ability than it is to have a specific playing style of your own. If you can master this skill set, you’ll find times when you can win with absolutely nothing in your own hand, and other occasions when you can make the toughest of laydowns – saving money in the process – because you are sure of your read and willing to release hands that might be the death of other players.
Your style might be tight in some situations, while it’s loose and aggressive against different opponents. This ability – to understand your opponent’s weaknesses and how to manipulate your own play to take advantage of those flaws – makes you difficult to defend against while putting your opponent in a position of having to make adjustments to his own game in order to play poker against you. When that happens, you might find that your opponent is out of his comfort zone and easier to exploit as a consequence.
The First Law of Hand Reading
You can begin the process of putting a player on a hand by making this assumption, and holding to it unless proven otherwise by a player under study. We’ll call it the first law of hand reading: The earlier a player’s position in the betting order, the narrower the range of hands he is probably holding.
When an early-position player calls a bet before the flop, he probably has a big pair, a couple of overcards, or has a small pair and is hoping to flop a set or get out if he doesn’t. In later positions, players are more likely to jump into the fray with a wider range of hole cards. That makes putting them on a hand more difficult. But it’s not impossible, and it can be done.
When push comes to shove, you really don’t have that many choices at the poker table, and each of them can provide information about your opponent’s hand:
If no one has bet,
- You can check.
- You can bet.
If there’s a bet before it’s your turn to act,
- You can fold.
- You can raise.
- You can call.
Assuming your opponent bets – and it’s a standard size bet, one he’d make with absolutely nothing or a pocket pair of Aces – you can begin to put him on a hand. Even though you won’t be able to determine the precise two cards he’s holding, some sort of hypothesis is far better than guessing.
Home on the Range
This hypothesis, this initial reckoning about what your opponent might be holding, is called a range. A range represents all the hands a player might have when he took that particular action. Let’s say he raises the blind from middle position, and based on what you’ve seen so far, you figure he’d make that play with any pair of fives or better, A-9 offsuit or better, A-8 suited or better, and K-Q.
You can use a shortcut for describing this range by writing: 5-5+, A-9o+, A-8s+, K-Q. In the simplest terms, you’ll want to fold your bad hands, re-raise with your good ones, and probably call with the kind of hands that offer huge implied odds as long as you have good reason to believe you can take his entire stack if you make a big hand. To do this, of course, both you and your opponent must have sufficiently sized stacks to make this kind of play worthwhile. If either of you is short stacked, the effective stack size – the amount of money you can possibly play for on this hand – is the smaller of the two stacks.
The message here is simple: Don’t play long shot drawing hands when you can’t possibly win enough to more than cover the long odds against completing your draw.
This is an oversimplified view of things to be sure, because even though you have a hand that is not toward the top portion of your opponent’s likely range of holdings, you might continue playing if you have reason to believe that a bluff on this or a succeeding round might win the pot. Even if you have a mediocre hand, one that you suspect will win the pot heads-up against this particular opponent only about 40 percent of the time if things went to a showdown, but you think a bluff would succeed 20 percent of the time, the combination of successful possibilities gives you a playable hand.
Walk a Mile in His Shoes
That first law of hand-reading, “The earlier a player’s position in the betting order, the narrower the range of hands he is probably holding,” is really a special case of putting yourself in your opponent’s shoes. If he raised from middle position, think about the hands he would need to have in order to raise in that spot.
When you do this, be wary of simply assuming your opponent would make that play with the same hands you would need if you were in his position. He might have a range similar to yours, but then again it might be very different. He could be a much tighter player, or he could be loose and aggressive – or he could vary his range depending on how he reads your playing style.
That’s one of poker’s complexities: He’s reading your hand while you’re reading his. And while you might be making a play contrary to one indicated solely by the strength of the cards in your hand, he might be doing the very same thing. Nevertheless, with every action your opponent takes, you should be able to narrow down his range of hands from your starting point to another, more precise point, where you can be more accurate about how you should play your hand in relation to the range of hands you believe he is holding.
If you think this process can get needlessly complicated, with wheels within wheels dizzily spinning, just disavow yourself of that assumption right now. While you might run into some very sophisticated players at the poker table, you won’t run into them very often unless you regularly play against the world’s best. For most situations you run into, the simplest explanation is most likely to be the correct one.
While there’s a lot of complexity in poker and deception is the rule rather than the exception, don’t make it too complicated or the only one you’re likely to fake out will be yourself.
Where to Look for Your Opponent’s Weaknesses
When you’re first starting to decipher a player’s style, pay particular attention to how he plays top pair with top kicker. It’s a very common hold’em hand, one that far too many of your opponents are going to play a bit more recklessly than they really should.
If you’re lucky, you’ll find opponents who are always willing to go all-in with top pair-top kicker as long as the board is not otherwise threatening. When you run into a player like this, make a note of it. You will eventually take all his chips and it shouldn’t take too long under normal circumstances. This is the guy you’ll want to play all your pairs against as long as the price is not too high. When you flop a set and he makes top pair, you’ve got him hooked. The same will happen if you can make a straight or a flush, or even two pair. You won’t need too many hands like this to turn almost any session into a winner.
You should also be very cognizant about how your opponent plays straight or flush draws. Does he try to get there as inexpensively as possible, or is he aggressive with them? Does his style depend on how many opponents he’s confronting, or whether he has additional outs – such as overcards – to go along with his draw? Some players are always prone to raise with their draws. Others aren’t. And some predicate their play on their assessment of their opponents, along with any other outs they might have, the number of opponents in the hand with them, and how that impacts their implied odds if they are fortunate enough to complete their hand.
The Second and Subsequent Laws of Hand Reading
If you know nothing about your opponent, you can start by making some assumptions about him or her. But don’t hold onto these assumptions once you begin to gather more information because the straw man you are constructing is unlikely to be exactly like the reality of the guy or gal across the table from you.
- Your opponent knows at least a little something about position and its importance at the poker table.
- Most of your opponents are not brain dead. They understand that each bet made is designed to accomplish something.
- If they over-bet the pot, they have a reason for it. A common reason for overbetting is to price draws out of the pot.
- If they under-bet, they have a reason for that too. Many players underbet to lure in callers, or make a smallish wager – called a blocking bet – that they expect their opponent to call. A blocking bet is usually made because it seems a better alternative than checking and having to call a bigger bet from your opponent.
- An opponent who calls a raise in late position usually has a speculative or drawing hand of some sort.
- When he re-raises, he usually has a big starting hand and wants to protect it.
Fear and No-Fear
These are opposite sides of the same coins. Some players always suspect monsters under the bed and will assign ranges to other players’ hands that make it almost impossible for them to call or raise, unless they hold the best possible hand at the time. That’s not putting a player on a hand; it’s taking yourself off of a hand – your hand, to be precise – and if you do it too often, you’ll find yourself without a bankroll to play with.
There are just some hands you’re bound to lose money with, and maybe go broke with altogether. That’s OK. Sometimes you can’t prevent losing your buy-in. But the stone cold nuts don’t come around all that often, and you can’t presume that monsters are always under the bed. In fact, most of the time, they’re not there at all.
Other poker players seem to always put their opponent on a range of hands they can beat most of the time, thereby giving themselves permission to play a wider variety of hands than they really ought to. Do not put your opponent on a hand by assuming he has to have a range of hands you can beat. You have to temper what you want to happen with the reality of what your adversary probably has, not what you hope he’s holding.
More than a few otherwise good players are lifelong money losers because they approach situations out of fear, while other lose out of unrealistic assumptions predicated on how weak they wish their opponent’s hand was.
Putting players on hands is not the application of any one particular skill. It’s using all the information at your disposal – observed tells, betting patterns, probability, and anything else you can factor into the equation – that helps you narrow down a large number of possible holdings into a reasonable few. Then you have to test your accuracy by following the hand attentively to its conclusion. It’s a formative process, to be sure, and the more you practice putting players on hand ranges the more accurate you’ll become.
And because any accurate read can save you an entire buy-in or win you one, an enormous amount of value accrues from learning and practicing this ability.
Related Lessons
By Lou Krieger
The author of many best-selling poker books, including “Hold’em Excellence” and “Poker for Dummies”. A true ambassador of the game and one of poker’s greatest ever teachers.
Poker in 2018 is as competitive as it has ever been. Long gone are the days of being able to print money playing a basic ABC strategy.
Today your average winning poker player has many tricks in their bags and tools in their arsenals. Imagine a soldier going into the heat of battle. Without his weapons, he is practically useless, and chances of survival are extremely low.
If you sit down at a poker table without any preparation or general understanding of poker fundamentals, the sharks are going to eat you alive. Sure you may get lucky once in a blue moon, but over the long term, things won’t end well.
With the evolution of poker strategy, you now have many tools at your disposal. Whether it be online poker training sites, free YouTube content, poker coaching, or poker vlogs, there’s no excuse to be a fish in today's game.
Some of the essential fundamentals you need to be utilizing that every poker player should have in their bag of tricks whether you are a Tournament or Cash Game Player are concepts such as hand combinations (Also known as hand combinatorics or hand combos).
Hand Combinations and Hand Reading
If you were to analyze a large sample of successful poker players you would notice that they all have one skill set in common: Hand Reading
What does hand reading have to do with hand combinations you might ask?
Well, poker is a game of deduction and to be a good hand reader, you need to be good at correctly ranging your opponents.
Once you have assigned them a range, you will then need to start narrowing that range down. Combinatorics is one of the ways we do this.
So what is combinatorics? It may sound like rocket science and it is definitely a bit more complex than some other poker concepts, but once you get the hang of combinatorics it will take your game to the next level.
Combinatorics is essentially understanding how many combos each of your opponent's potential holdings are and deducing their potential holdings utilizing concepts such as removal and blockers.
There are 52 cards in a deck, 13 of each suit, and 4 of each rank with 1326 poker hands in total. To simplify things just focus on memorizing all of the potential combos to start:
- 16 possible hand combinations of every unpaired hand
- 12 combinations of every unpaired offsuit hand
- 4 combinations of each suited hand
- 6 possible combinations of pocket pairs
Here is a short video example of using combinatorics to count the number of ways a non-paired hand AK can be arranged (i.e. how many combos there are):
So now that we have this memorized, let's look at a hand example and how we can apply combinatorics in game.
We hold A♣Q♣ in the SB and 3bet the BTN’s open to 10bb with 100bb stacks. He flats and we go heads up to a flop of
A♠ 5♦ 4♦
We check and our opponent checks back with 21bb in the middle
Turn is the 4♥
We bet 10bb and our opponent calls for a total pot of 41bb
The river brings the 9♠
So the final board reads
A♠ 5♦ 4♦ 4♥ 9♠
We bet 21bb and our opponent jams all in leaving us with 59bb to call into a pot of 162bb resulting in needing at least 36% pot equity to win.
Our opponent is representing a polarized range here. He is either nutted or representing missed draws so we find ourself in a tough spot. This is where utilizing combinatorics to deduce his value hands vs bluffs come into play. Now we need to narrow down his range given our line and his line. Let's take a look at how we do this...
Free MTT Poker Training:
The Underused MTT Skills Essential For Success
- 5 Day Email MTT Poker Training Course By Poker Pro Kelvin 'Acesup' Beattie
- 3 Key Skills That Will Take Your MTT Poker Game To A New Level
- 1.5 Hours Of Professional Poker Training
Blockers and Card Removal Effects
First, let's take a look at the hands we BLOCK and DON’T BLOCK
Since we hold an Ace in our hand and there is an Ace on the board, that only leaves 2 Ace’s left in the deck. So there is exactly 1 combo of AA.
We BLOCK most of the Aces he can be holding, so we can REMOVE some Aces from his range.
We do not BLOCK the A♦ as we hold A♣Q♣, and the A on the board is a spade, so it is still possible for him to have some A♦x♦ hands.
We checked flop to add strength to our check call range (although a bet with a plan to triple barrel is equally valid in this situation SB vs BTN) and because of this our opponent may not put us on an A here.
If he is a thinking player his jam can exploit our thin value bet on the river turning his missed straight/flush draws into a bluff to get us to fold our big pocket pairs and even make it a tough call with our perceived weak holdings.
The problem in giving him significant credit for this part of his bluffing range is the question of would he really shove here with good SDV (Showdown Value)?
These are the types of questions we must ask ourselves to further deduce his range along with applying the combinatoric information we now have.
Poker Hand Reading Practice
Now, let's look at all the nutted Ax hands our opponent can have.
If he has a nutted hand like A4 or A5, and we assume he is only calling 3bets with Axs type hands, the only suited combo of those hands he can have are exactly A♥5♥. He can’t have A♦5♦ or A♦4♦ because the 4 and the 5 are both diamonds on the board blocks these hands.
Learn To Play Poker Beginner
Lets take a look at all of this value hands:
There is only 1 combo of 44 left in the deck, 2 combos of A9s, 3 Combos of 55, 3 Combos of 99, 2 Combos of 45s - some of these hands may also be bet on the flop when facing a check.
So to recap we have:
1 Combo A5s, 2 Combos of A9s, 3 Combos of 55 (With one 5 on board, the number of combinations of 55 are cut in half from 6 combos to 3 combos), 1 Combo of 44, 2 Combos of 45s, 3 Combos of 99
Total: 12 Value Combos
Now we need to look at our opponent's potential bluffs
Based on the villain's image, this is the range of bluffs we assigned him:
K♦Q♦(1 Combo), J♦T♦ (1 Combo), T♦9♦ (1 Combo), 67s (4 Combos)
He may also turn some other random hands with little showdown value into bluffs such as A♦2♦/A♦3♦
Total: 9 Bluff Combos
9(Bluff Combos) + 12(Value Combos) = 22
9/21 = 42% of the time our opponent will be bluffing (assuming he always bets this entire range)
11/21 = 58% of the time our opponent will be value raising
Now, this is the range we assigned him in game based on the action and what we perceived our opponents range to be.
We are not always correct in applying the exact range of his potential holdings, but so long as you are in the ballpark of that range you can still make quite a few deductions to put yourself in the position to make the correct final decision.
According to the range we assigned him, he has 11 Value Combos and 9 Bluff Combos which gives us equity of 42%. This would result in a positive expected value call as we only need 36% pot odds to call.
However, unless you are playing against very tough opponents you will not see someone bluffing all 9 combos we have assigned - most likely they will bluff in the range of 4-6 combos on average which gives equity in the range of 20-30% equity. This is not enough to call.
We ultimately made our decision based on the fact that we felt our opponent was much less likely to jam with his bluffs in this spot. Given that it was already a close decision to begin with, we managed to find what ended up being the correct fold.
Now this all may seem a bit overwhelming, but if you just start taking an extra minute on your big decisions you’d be surprised how quickly you can actually process all this information on this spot.
A good starting point is to simply memorize all of the possible hand combinations listed above near the beginning of the article.
Get access to our 30-minute lesson on Combinatorics and PokerStove by clicking on one of the buttons below:
Conclusion On Combinatorics
How To Read Hands In Poker
Eventually accounting for your opponent's combos in a hand will become second nature. To get to the point that , a lot of the work needs to be done off the table and in the lab. As you spend more time studying it and reviewing hand histories like the one above, you will find yourself intuitively and almost subconsciously using combinatorics in your decision making tree.
But the work will be worth the effort, as being able to count combos on the fly will add a new dimension to your game, allow you to make more educated decisions, become a tougher opponent to play against and move away from playing ABC poker.
How To Read Palms Hands Psychic
Want more content like the ones in this blog post on poker combinatorics? Check out our Road to Success Course where we have almost 100 videos like this to help take your game to the next level. You can also get the first module of the Road To Success Course for Free - for more details see the free poker training videos page by TopPokerValue.com.